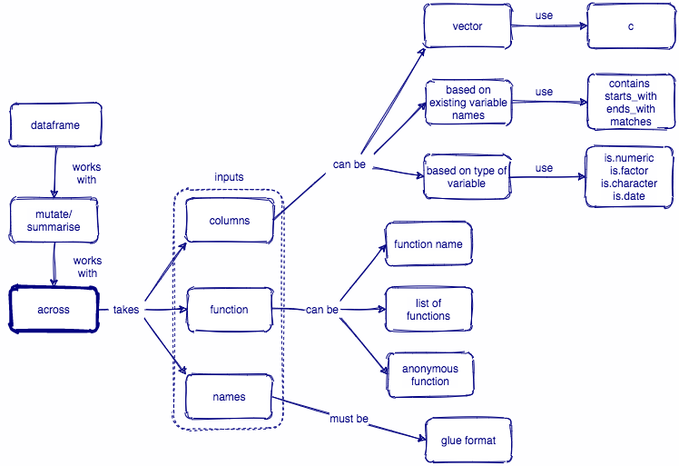
Column-wise operations with dplyr:
Old and New
Brendan Cullen
RStudio Certified Trainer
bcullen.rbind.io | _bcullen | brendanhcullen
Slides: columnwise-operations-dplyr.netlify.app
Concept map
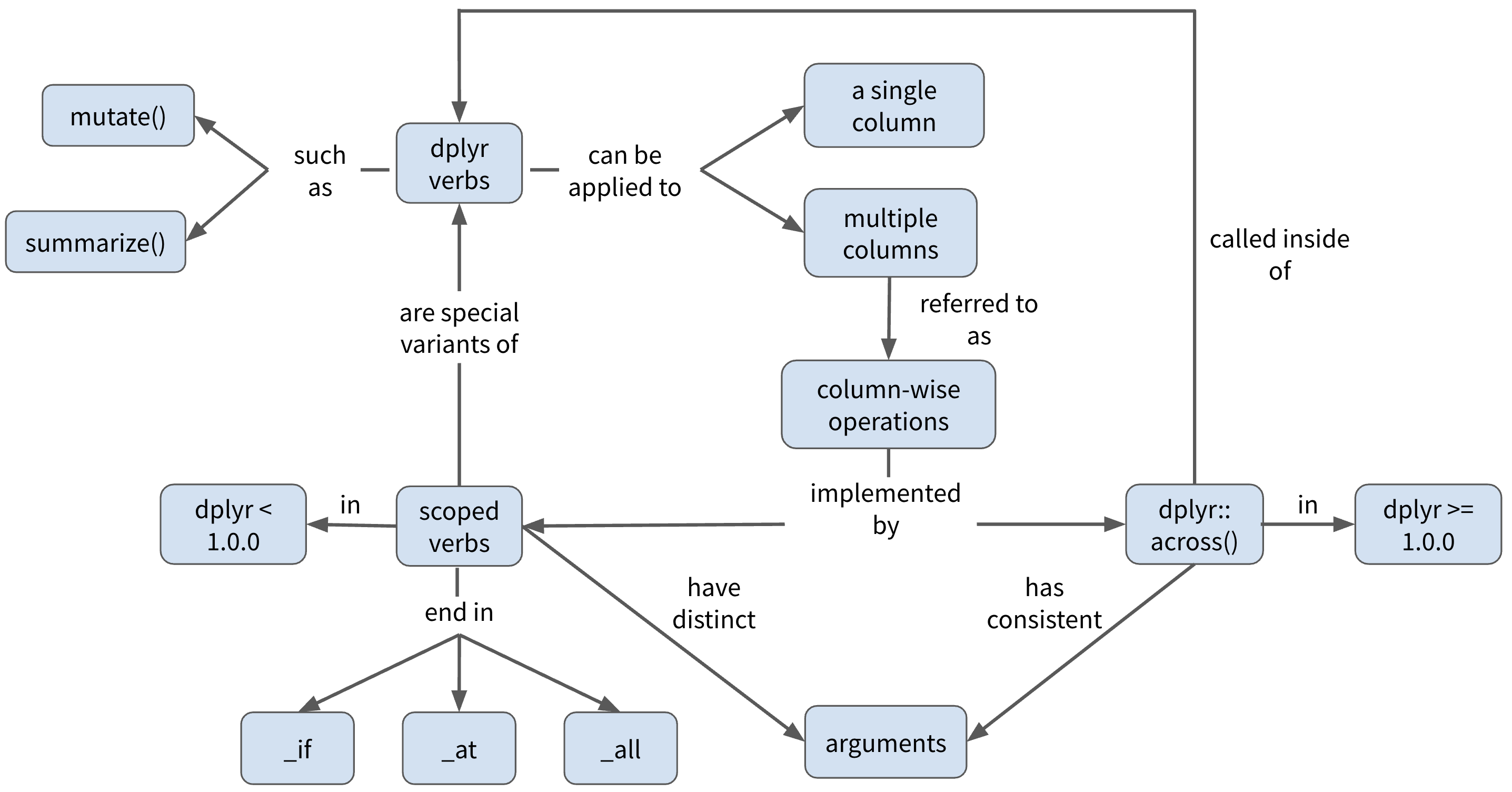
Learning objectives
Learning objectives
- Review how to apply
dplyrfunctions, e.g.mutate(),summarize(), to single columns
Learning objectives
- Review how to apply
dplyrfunctions, e.g.mutate(),summarize(), to single columns
Learn how to perform column-wise operations two ways:
scoped verbs, e.g.
summarize_at(),summarize_if(), etc...across()fromdplyr1.0.0
Learning objectives
- Review how to apply
dplyrfunctions, e.g.mutate(),summarize(), to single columns
Learn how to perform column-wise operations two ways:
scoped verbs, e.g.
summarize_at(),summarize_if(), etc...across()fromdplyr1.0.0
- Apply
across()to summarize multiple columns of data
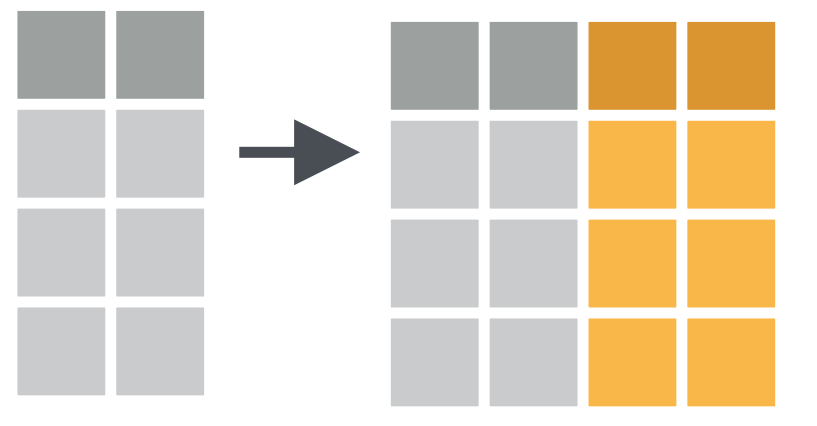
Column-wise operations
Column-wise operations refers to applying the same dplyr verbs (or other data transformation functions) to multiple columns simultaneously.
Column-wise operations
Column-wise operations refers to applying the same dplyr verbs (or other data transformation functions) to multiple columns simultaneously.
e.g. Create multiple new columns with mutate()
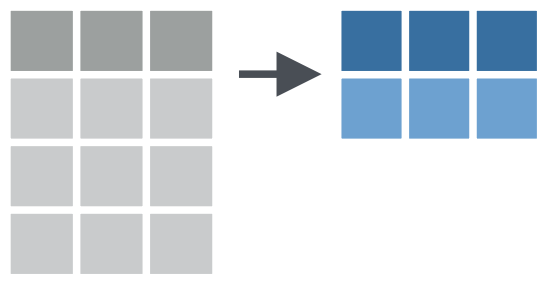
Column-wise operations
Column-wise operations refers to applying the same dplyr verbs (or other data transformation functions) to multiple columns simultaneously.
e.g. Create multiple new columns with mutate()

e.g. Summarize multiple columns with summarize()
Palmer Penguins
library(palmerpenguins)library(tidyverse)glimpse(penguins)## Rows: 344## Columns: 8## $ species <fct> Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adeli…## $ island <fct> Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgerse…## $ bill_length_mm <dbl> 39.1, 39.5, 40.3, NA, 36.7, 39.3, 38.9, 39.2, 34.1, 42.0, 37.8, 37.8, 41.1, 38.6, 34.…## $ bill_depth_mm <dbl> 18.7, 17.4, 18.0, NA, 19.3, 20.6, 17.8, 19.6, 18.1, 20.2, 17.1, 17.3, 17.6, 21.2, 21.…## $ flipper_length_mm <int> 181, 186, 195, NA, 193, 190, 181, 195, 193, 190, 186, 180, 182, 191, 198, 185, 195, 1…## $ body_mass_g <int> 3750, 3800, 3250, NA, 3450, 3650, 3625, 4675, 3475, 4250, 3300, 3700, 3200, 3800, 440…## $ sex <fct> male, female, female, NA, female, male, female, male, NA, NA, NA, NA, female, male, m…## $ year <int> 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2…Column-wise operations
Let's review...
Apply summarize() to a single column.
Column-wise operations
Let's review...
Apply summarize() to a single column.

🤔 Use summarize() to calculate the mean bill length for each species in penguins
❓ What function do you need to include before summarize() in order to calculate means for each species?

Artwork by @allison_horst
penguins %>% group_by(species) %>% summarize(bill_length_mm = mean(bill_length_mm, na.rm = TRUE))## # A tibble: 3 x 2## species bill_length_mm## <fct> <dbl>## 1 Adelie 38.8## 2 Chinstrap 48.8## 3 Gentoo 47.5Column-wise operations
Apply summarize() to multiple columns at once

Column-wise operations
Apply summarize() to multiple columns at once

🤔 Calculate the mean bill length and bill depth for each species
🚫 Avoid copying and pasting or repeating mean() more than once in your solution
Artwork by @allison_horst
penguins %>%
group_by(species) %>%
summarize_at(vars(c(bill_length_mm, bill_depth_mm)),
mean, na.rm = TRUE)
🔍 summarize_at() is an example of a scoped verb. It is a special variant of summarize() that applies a summary function to a specific set of columns.
⚠️ When using scoped verbs ending in _at() you must use vars() to select columns.
❓ How many columns will be in our output?
## # A tibble: 3 x 3## species bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm## <fct> <dbl> <dbl>## 1 Adelie 38.8 18.3## 2 Chinstrap 48.8 18.4## 3 Gentoo 47.5 15.0Column-wise operations
Apply summarize() to multiple columns at once

🤔 Calculate the mean of all numeric variables for each species.
🚫 Again, no copying and pasting or repeating mean() more than once!
penguins %>%
group_by(species) %>%
summarize_if(is.numeric, mean, na.rm = TRUE)
🔍 summarize_if() is another example of a scoped verb. It is a special variant of summarize() that applies a summary function to a set of columns that all satisfy some logical criteria.
🔍 That logical criteria is specified using a predicate function, e.g. is.numeric(), which will return TRUE or FALSE.
## # A tibble: 3 x 6## species bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g year## <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>## 1 Adelie 38.8 18.3 190. 3701. 2008.## 2 Chinstrap 48.8 18.4 196. 3733. 2008.## 3 Gentoo 47.5 15.0 217. 5076. 2008.A better way?
dplyr < 1.0.0

summarize_at(), summarize_if(), summarize_all(), mutate_if(), mutate_at(), mutate_all(), ...
😓
A better way?
dplyr < 1.0.0

summarize_at(), summarize_if(), summarize_all(), mutate_if(), mutate_at(), mutate_all(), ...
😓
dplyr >= 1.0.0

across()
😎
dplyr::across()
 Artwork by @allison_horst
Artwork by @allison_horst
dplyr::across()
 Artwork by @allison_horst
Artwork by @allison_horst
dplyr::across()
across(.cols, .fns, ..., .names)
dplyr::across()
across(.cols, .fns, ..., .names)
.cols = the columns you want to transform
dplyr::across()
across(.cols, .fns, ..., .names)
.cols = the columns you want to transform
.fns = the function(s) you want to apply to each of the selected columns
dplyr::across()
across(.cols, .fns, ..., .names)
.cols = the columns you want to transform
.fns = the function(s) you want to apply to each of the selected columns
... = additional arguments for the function(s) specified in .fns (e.g. na.rm = TRUE)
dplyr::across()
across(.cols, .fns, ..., .names)
.cols = the columns you want to transform
.fns = the function(s) you want to apply to each of the selected columns
... = additional arguments for the function(s) specified in .fns (e.g. na.rm = TRUE)
.names = how you want to name the output columns. Here, "{col}" is a special placeholder for the input column name, and you can add any suffix you want to it
dplyr::across()
across(.cols, .fns, ..., .names)
.cols = the columns you want to transform
.fns = the function(s) you want to apply to each of the selected columns
... = additional arguments for the function(s) specified in .fns (e.g. na.rm = TRUE)
.names = how you want to name the output columns. Here, "{col}" is a special placeholder for the input column name, and you can add any suffix you want to it
- e.g. When calculating the mean of the
yearcolumn, specifying.names = "{col}_mean"would result in an output column named"year_mean"
dplyr::across()
across(.cols, .fns, ..., .names)
🤔 Use across() to calculate the mean of all numeric columns for each species in penguins
📣 Remember, across() goes inside of the dplyr function that you want to apply to multiple columns.
penguins %>%
group_by(species) %>%
summarize(across(where(is.numeric),
mean,
na.rm = TRUE,
.names = '{col}_mean'))
🔍 where() is an example of a tidyselect helper function, like starts_with() or contains().
It selects the variables for which some predicate function , such as is.numeric() , returns TRUE.
## # A tibble: 3 x 6## species bill_length_mm_mean bill_depth_mm_mean flipper_length_mm_mean body_mass_g_mean year_mean## <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>## 1 Adelie 38.8 18.3 190. 3701. 2008.## 2 Chinstrap 48.8 18.4 196. 3733. 2008.## 3 Gentoo 47.5 15.0 217. 5076. 2008.👀 Notice that all of the output variables have the suffix "_mean".
penguins %>%
group_by(species) %>%
summarize(across(where(is.numeric),
list(mean = mean),
na.rm = TRUE))
🔍 If you specify .funs as a named list, e.g. list(mean = mean), then across() will automatically append the name of the applied function(s) to the names of the output columns.
This way you don't have to manually specify a .names argument at all!
## # A tibble: 3 x 6## species bill_length_mm_mean bill_depth_mm_mean flipper_length_mm_mean body_mass_g_mean year_mean## <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>## 1 Adelie 38.8 18.3 190. 3701. 2008.## 2 Chinstrap 48.8 18.4 196. 3733. 2008.## 3 Gentoo 47.5 15.0 217. 5076. 2008.👀 Same exact output as before!
Concept map

More resources
- Blog post by Hadley Wickham highlighting
across()as a key component of thedplyr1.0.0 update.
- This vignette on tidyverse.org about column-wise operations.
- Two blog posts by Rebecca Barter on scoped verbs and
across().
- Interactive tutorial by Ted Laderas on
tidyselectand a full list of selection helpers.